An emotion triggered by stress or perceived threats, the common response is anxiety. For some people, however, it becomes chronic, surpassing simple sporadic worry or fear. Being knowledgeable about what causes it, how to recognize symptoms, and when to seek help are the essential steps toward the effective management of anxiety.
What Is Anxiety?
An anxiety response is a normal response to stress that might be characterized by feelings of tension, fear, or apprehension. Although normal and sometimes adaptive – preparing for an important exam or presentation, for example – chronic and excessive anxiety interferes with daily life.

Causes of Anxiety
Biological Factors
Genetics might play a role because anxiety disorders often seem to run in families. Imbalances of certain chemicals in the brain, including serotonin and dopamine, can also cause or contribute to anxiety.
Environmental Stressors
Stressful events, such as the loss of a job, financial difficulty, or trouble with a relationship, may trigger or contribute to anxiety. Traumatic events, especially in childhood, also increase vulnerability.
Personality Traits
People who are naturally more sensitive or perfectionistic tend to be more susceptible to anxiety.
Medical Conditions
Sometimes, stress can be an effect of some medical conditions like heart diseases and thyroid problems, as well as medication side effects.
Anxiety Symptoms
Anxiety may vary from individual to individual, but most of them experience the following symptoms:
- Physical Symptoms
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating or trembling
- Tense muscles
- Abdominal pain or nausea
- Emotional Symptoms
- Anxiety or fear that one cannot control
- Irritability or being on the edge
- Cannot concentrate
- Feeling some disaster is lurking nearby
- Behavioral Symptoms
- Avoidance of situations that bring anxiety
- Difficulty in keeping relationships
- Pacing or restlessness
Types of Anxiety Disorders
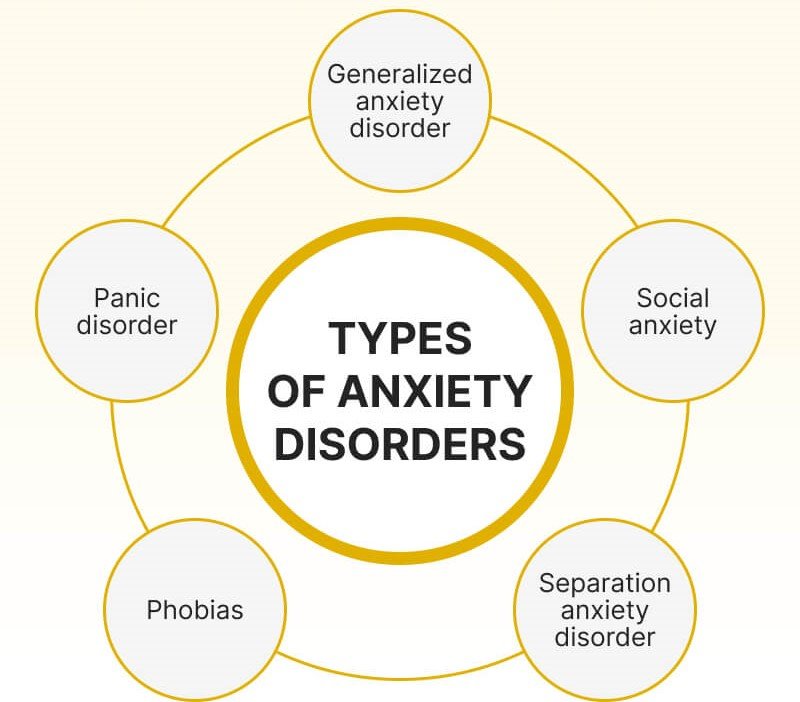
There are many specific categories of anxiety disorders, including the following:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Excessive concern about everyday things over a period of time.
- Panic Disorder: Panic attacks occur frequently with no apparent precipitating cause.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: A degree of fear related to the potential for social or performance-related judgments.
- Phobias: One type of irrational fear of particular objects or situations.
When to Seek Professional Help
Mild anxiety can be managed through modifications to lifestyle habits, but treatment by a professional is always necessary if:
- Anxiety conditions interfere with work, school, or other close relationships.
- You have panic attacks that occur very frequently and that you could not control.
- You have either chest pain or severe headaches at least a few days a week.
- You are afraid and, therefore, avoid places or activities.
- Anxiety causes you to feel hopelessness or suicide ideation.
- Treatment of Anxiety
- Anxiety is curable and there are many nice remedies for this condition:
- Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Identifies and changes negative thought patterns that cause anxiety.
- Exposure Therapy: Gradual exposure to feared situations.
- Medication
Treatment Options for Anxiety
Anxiety is treatable, and several effective options are available:
- Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps identify and change thought patterns contributing to anxiety.
- Exposure therapy Gradually desensitizes individuals to feared situations.
- Medication
- Anti-anxiety medications like benzodiazepines or SSRIs may be prescribed for moderate to severe cases.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can significantly reduce anxiety.
- Mindfulness techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises offer immediate calming effects.
- Support Groups
Sharing experiences and coping strategies with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional relief.
Conclusion
Anxiety can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to control your life. Understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step toward seeking help and finding effective treatment. Whether through therapy, medication, or lifestyle adjustments, there are many ways to manage anxiety and regain peace of mind.
If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider or mental health professional. Taking that first step can make all the difference.
Treatment Options for Anxiety
Anxiety is treatable, and several effective options are available:
- Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps identify and change thought patterns contributing to anxiety.
- Exposure therapy Gradually desensitizes individuals to feared situations.
- Medication
- Anti-anxiety medications like benzodiazepines or SSRIs may be prescribed for moderate to severe cases.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can significantly reduce anxiety.
- Mindfulness techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises offer immediate calming effects.
- Support Groups
Sharing experiences and coping strategies with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional relief.
Conclusion
Anxiety can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to control your life. Understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step toward seeking help and finding effective treatment. Whether through therapy, medication, or lifestyle adjustments, there are many ways to manage anxiety and regain peace of mind.
If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider or mental health professional. Taking that first step can make all the difference.

